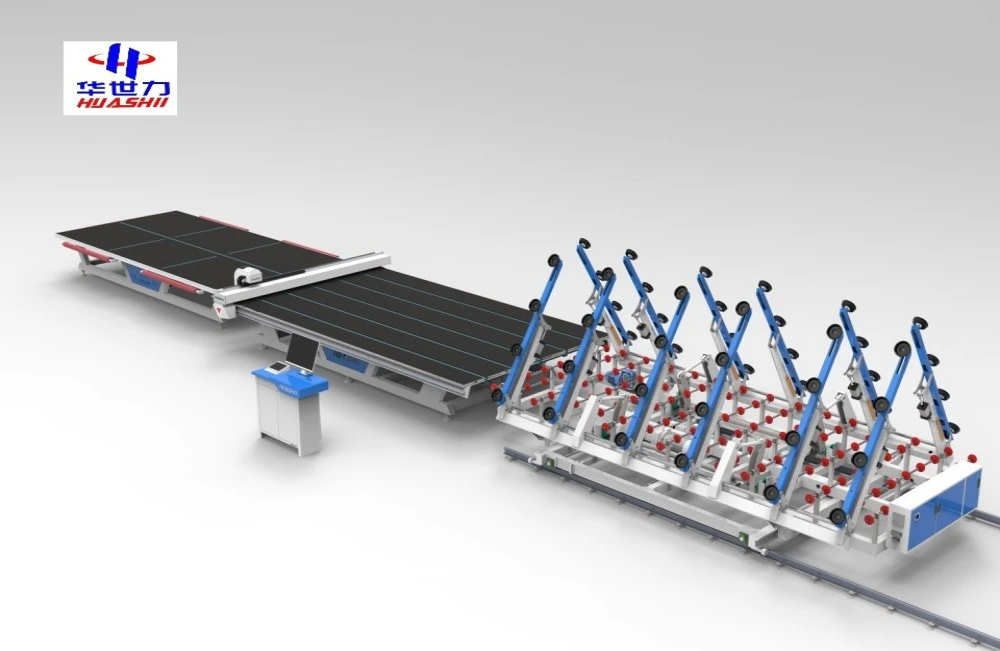
An automatic glass cutting assembly line represents a revolutionary advancement in glass processing technology, combining precision CNC machinery with intelligent automation to transform how manufacturers approach glass fabrication. This sophisticated system integrates multiple cutting stations, material handling robotics, and quality control mechanisms to deliver consistent, high-precision cuts across various glass types and thicknesses. By eliminating manual intervention and optimizing workflow processes, these automated systems enable manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency while maintaining exceptional quality standards that meet the demanding requirements of architectural, automotive, and specialty glass applications.
Understanding Automatic Glass Cutting Assembly Lines
The modern glass processing industry demands precision, speed, and consistency that traditional manual cutting methods simply cannot deliver. An automatic glass cutting assembly line represents the pinnacle of glass fabrication technology, integrating advanced CNC machinery with intelligent automation systems to create a seamless production workflow.
These sophisticated systems utilize computer-controlled cutting heads equipped with diamond wheels or laser cutting technology to achieve precise cuts with tolerances as tight as ±0.1mm. The assembly line configuration allows multiple glass sheets to be processed simultaneously, dramatically increasing throughput compared to standalone cutting machines.
What sets these systems apart is their ability to handle diverse glass types, from standard float glass to tempered, laminated, and specialty coated materials. The automated material handling components ensure smooth transport between cutting stations while minimizing the risk of damage or contamination that often occurs with manual handling.
Smart factory integration capabilities allow these lines to communicate with enterprise resource planning systems, enabling real-time production monitoring and predictive maintenance scheduling. This connectivity ensures optimal operational efficiency and helps manufacturers maintain consistent quality standards across all production runs.
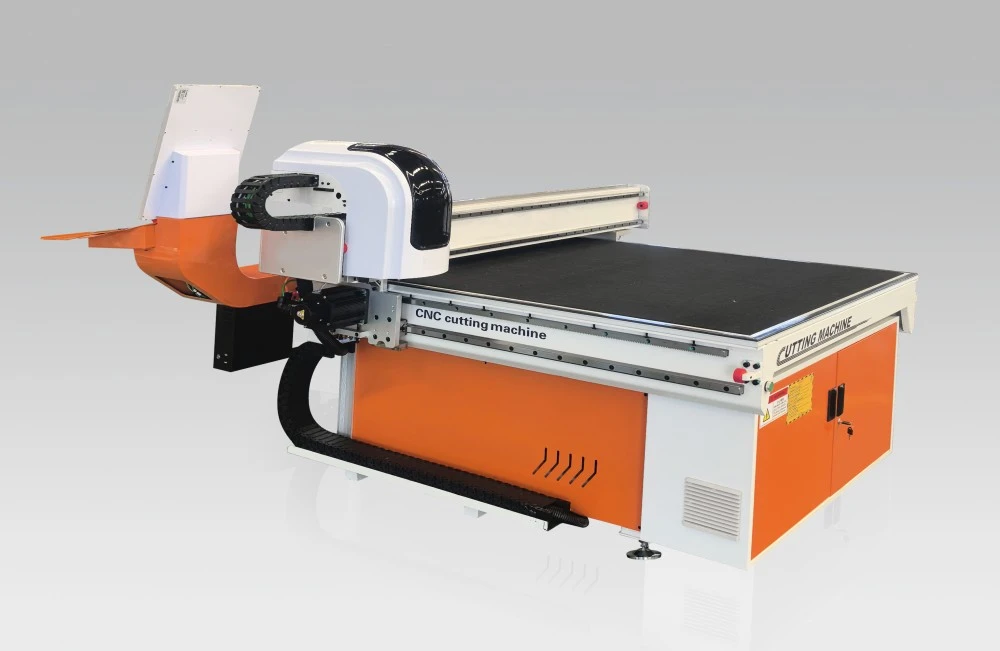
Industry Challenges and Manufacturing Needs
Glass manufacturers face mounting pressure to increase production capacity while maintaining stringent quality requirements. Traditional cutting methods often result in material waste rates exceeding 15%, significantly impacting profitability and sustainability goals. Labor costs continue to rise, making manual cutting operations increasingly uneconomical.
The architectural glass sector requires precise dimensional accuracy for curtain wall installations, where even minor variations can compromise structural integrity. Automotive glass production demands consistent edge quality to ensure proper sealing and safety performance. These requirements push manufacturers toward automation solutions that can deliver repeatable results.
Quality control challenges plague manual operations, where human error can lead to costly rework or customer rejections. Inconsistent cutting speeds and pressure application often result in edge chipping, stress concentrations, and dimensional variations that affect downstream processing operations.
Production scheduling becomes complex when dealing with multiple glass types and sizes, particularly for custom architectural projects. Manual systems struggle to accommodate rapid changeovers between different specifications, leading to extended setup times and reduced overall equipment effectiveness.
Safety concerns also drive automation adoption, as manual glass handling exposes workers to cut hazards and repetitive strain injuries. Automated systems eliminate these risks while creating a safer working environment that complies with modern industrial safety standards.
Advanced Features and Operational Capabilities
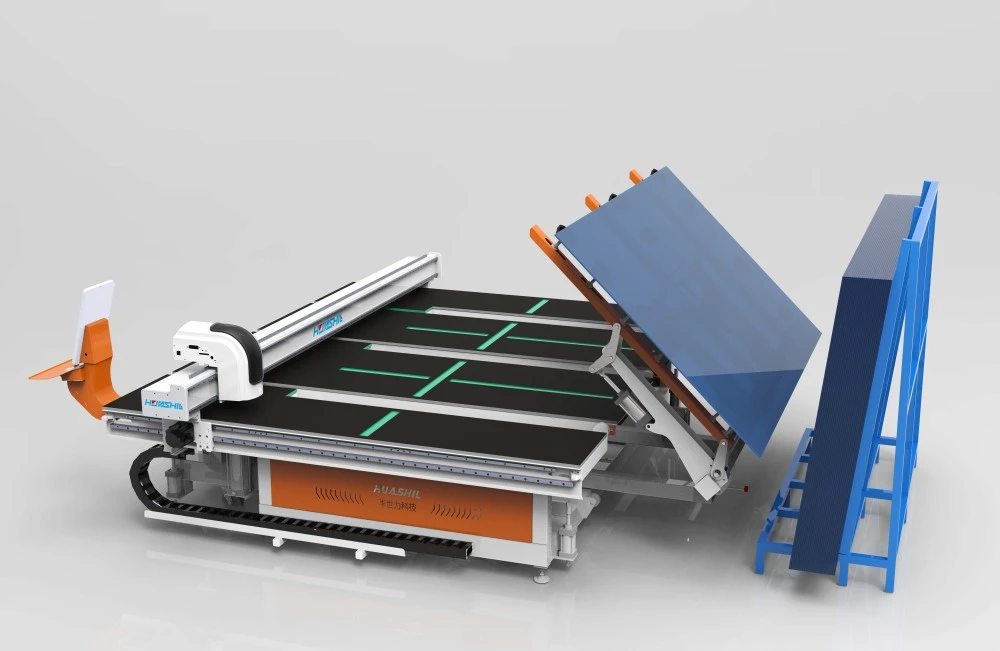
Modern automatic glass cutting assembly lines incorporate sophisticated features designed to maximize productivity and precision. Multi-head cutting systems enable simultaneous processing of multiple glass sheets, effectively multiplying production capacity without proportional increases in floor space requirements.
Intelligent nesting software optimizes material utilization by calculating the most efficient cutting patterns, reducing waste to less than 5% in many applications. This optimization considers not only dimensional requirements but also grain direction, stress patterns, and edge finishing specifications.
Adaptive cutting parameters automatically adjust based on glass thickness, type, and cutting requirements. Pressure sensors monitor cutting wheel condition and automatically compensate for wear, ensuring consistent cut quality throughout the production run. When wheel replacement becomes necessary, the system alerts operators and can even perform automatic tool changes on advanced models.
Integrated inspection systems utilize high-resolution cameras and laser measurement devices to verify dimensional accuracy and edge quality in real-time. Defective pieces are automatically identified and diverted to separate handling areas, preventing downstream processing of non-conforming materials.
Environmental control systems maintain optimal cutting conditions by managing temperature, humidity, and cutting fluid application. These systems ensure consistent performance regardless of ambient conditions and extend cutting tool life through proper lubrication and cooling.
Flexible conveyor systems accommodate various glass sizes and shapes, from standard rectangular sheets to complex curved profiles. Vacuum handling systems provide secure grip without marking or damaging delicate surface coatings, while pneumatic positioning ensures precise alignment for cutting operations.

Technology Integration and Control Systems
The technological foundation of automatic glass cutting assembly lines relies on advanced motion control systems that coordinate multiple axes with sub-millimeter precision. Servo-driven cutting heads maintain constant velocity and pressure, eliminating the variations inherent in manual operations.
Machine learning algorithms continuously analyze cutting performance data to optimize parameters and predict maintenance requirements. These systems learn from historical data to improve cutting strategies and reduce cycle times while maintaining quality standards.
Human-machine interfaces provide intuitive operation through touchscreen controls and graphical programming environments. Operators can easily configure cutting patterns, adjust parameters, and monitor system performance without requiring extensive technical training.
Safety systems incorporate multiple layers of protection, including light curtains, emergency stops, and automated shutdown procedures. These systems ensure operator safety while minimizing production disruptions during maintenance or setup activities.
Communication protocols enable seamless integration with existing manufacturing execution systems, allowing real-time data exchange and production tracking. This connectivity supports lean manufacturing initiatives and provides visibility into production metrics that drive continuous improvement efforts.
Remote monitoring capabilities allow technical support teams to diagnose issues and provide assistance without on-site visits, reducing downtime and maintenance costs. Cloud-based data storage enables performance trending and benchmarking across multiple production facilities.
Competitive Advantages and Performance Benefits
Automatic glass cutting assembly lines deliver substantial performance improvements over traditional cutting methods. Production speeds typically increase by 200-400%, while material waste decreases significantly through optimized nesting and consistent cutting quality.
Labor cost reductions often justify automation investments within 18-24 months, as a single operator can manage multiple cutting lines simultaneously. This efficiency gain allows manufacturers to reallocate skilled workers to higher-value activities such as quality control and process optimization.
Consistency represents perhaps the most significant advantage, as automated systems eliminate human variability in cutting parameters. This reliability enables manufacturers to offer tighter tolerances and improved quality guarantees to customers, supporting premium pricing strategies.
Energy efficiency improvements result from optimized cutting patterns and reduced material handling requirements. Modern systems consume 30-40% less energy per unit produced compared to traditional manual operations, supporting sustainability goals and reducing operating costs.
Flexibility advantages become apparent when handling diverse product mixes or custom orders. Automated systems can switch between different cutting patterns within minutes, compared to hours required for manual reconfiguration.
Documentation and traceability capabilities support quality management systems and customer requirements for material certification. Automated data collection eliminates transcription errors and provides complete production history for each glass sheet processed.
Implementation Considerations and Limitations
Capital investment requirements represent the primary barrier to automation adoption, with complete systems ranging from $200,000 to over $1 million depending on complexity and capacity requirements. Manufacturers must carefully evaluate return on investment based on production volumes and labor costs.
Technical expertise requirements extend beyond basic machine operation to include programming, maintenance, and troubleshooting capabilities. Organizations may need to invest in training programs or recruit specialized personnel to support automated systems effectively.
Facility modifications often become necessary to accommodate automated systems, including electrical upgrades, compressed air systems, and environmental controls. Floor space requirements may exceed those of manual operations due to material handling and safety clearances.
Product limitations exist for certain specialty glass types or extremely small production runs where setup time exceeds processing time. Some decorative glass applications with complex patterns may still require manual intervention or specialized tooling.
Maintenance requirements, while predictable, require scheduled downtime and spare parts inventory management. Preventive maintenance programs become critical to avoid unexpected production interruptions and maintain system performance.
Integration challenges may arise when connecting automated systems to existing production workflows or quality management systems. Careful planning and potentially custom software development may be required to achieve seamless operation.
Market Comparison and Technology Positioning
The automatic glass cutting assembly line market features several established manufacturers, each offering distinct technological approaches and capabilities. European manufacturers traditionally emphasize precision engineering and advanced automation features, while Asian suppliers often focus on cost-effectiveness and rapid deployment.
Cutting technology variations include mechanical scoring with diamond wheels, laser cutting systems, and waterjet processing. Each approach offers specific advantages depending on glass type, thickness, and edge quality requirements. Mechanical systems excel in high-volume production environments, while laser technology provides superior precision for complex shapes.
Control system sophistication varies significantly between suppliers, with some offering basic programmable logic controllers while others provide full industrial computer systems with advanced analytics capabilities. The choice often depends on integration requirements and desired automation levels.
Service and support capabilities represent crucial differentiators, particularly for international suppliers. Local service availability, spare parts inventory, and technical support responsiveness significantly impact total cost of ownership and production reliability.
Customization capabilities distinguish premium suppliers from commodity providers. The ability to modify standard systems for specific applications or integrate with existing equipment often justifies higher initial costs through improved operational efficiency.
Technology roadmaps and upgrade paths become important considerations for long-term investments. Suppliers with strong research and development capabilities can provide system upgrades that extend equipment life and maintain competitive performance levels.
Target Applications and Industry Sectors
Architectural glass fabrication represents the largest market segment for automatic glass cutting assembly lines, driven by increasing demand for energy-efficient building facades and complex geometric designs. Curtain wall manufacturers require precise cutting capabilities to ensure proper fit and structural performance in high-rise construction projects.
Automotive glass production utilizes specialized cutting systems designed for complex curved shapes and stringent safety requirements. These applications demand exceptional edge quality and dimensional accuracy to ensure proper sealing and crash performance characteristics.
Furniture and decorative glass manufacturers benefit from the flexibility to process diverse shapes and sizes efficiently. The ability to handle small batch sizes economically makes automation attractive for custom furniture producers and architectural glazing contractors.
Smart mirror and display glass applications require precise cutting of coated substrates without damaging functional layers. Specialized handling systems and cutting parameters ensure proper electrical connectivity and optical performance in finished products.
Industrial glass components for appliances, lighting, and electronics demand consistent quality and tight tolerances. Automated cutting systems provide the repeatability necessary for high-volume production while maintaining quality standards required for consumer products.
Specialty glass applications, including optical components and scientific instruments, often require custom cutting solutions with enhanced precision capabilities. These niche markets justify premium automation systems with advanced metrology and quality control features.
Conclusion and Future Outlook
Automatic glass cutting assembly lines represent a transformative technology that addresses critical challenges in modern glass manufacturing. These systems deliver substantial improvements in productivity, quality, and operational efficiency while reducing labor costs and material waste.
The technology continues evolving toward greater intelligence and connectivity, with artificial intelligence and machine learning driving further optimization opportunities. As Industry 4.0 principles gain adoption, these systems will become integral components of smart manufacturing ecosystems that deliver unprecedented levels of performance and flexibility.
FAQ
Q1: What is the typical payback period for an automatic glass cutting assembly line investment?
A: Most manufacturers experience payback periods between 18-36 months, depending on production volumes, labor costs, and material waste reduction. High-volume operations often achieve faster returns through increased throughput and reduced operating expenses.
Q2: Can automatic glass cutting systems handle different glass types and thicknesses?
A: Yes, modern systems accommodate glass thicknesses from 2mm to 25mm and various types including float, tempered, laminated, and coated glass. Automatic parameter adjustment ensures optimal cutting performance for each material specification.
Q3: What maintenance requirements are associated with automated glass cutting equipment?
A: Routine maintenance includes daily cleaning, weekly lubrication, and periodic cutting wheel replacement. Comprehensive preventive maintenance programs typically require 4-8 hours monthly, with major servicing scheduled annually to maintain optimal performance.
Experience HUASHIL's Advanced Glass Processing Solutions
HUASHIL stands as a premier automatic glass cutting assembly line manufacturer, delivering cutting-edge automation solutions that transform glass processing operations worldwide. Our comprehensive product portfolio addresses the diverse needs of architectural, automotive, and specialty glass manufacturers through innovative engineering and reliable performance.
Drawing from extensive experience in automated machinery development, we understand the unique challenges facing glass processors in today's competitive marketplace. Our engineering team collaborates closely with customers to develop customized solutions that optimize productivity while maintaining the highest quality standards.
The HUASHIL advantage extends beyond equipment supply to encompass complete project support, including installation, training, and ongoing technical assistance. Our global service network ensures rapid response to customer needs, minimizing downtime and maximizing production efficiency.
Quality assurance remains paramount in our manufacturing processes, with rigorous testing protocols ensuring each system meets specified performance criteria before shipment. This commitment to excellence has earned recognition from leading glass manufacturers across multiple continents.
Whether you're planning a new production facility or upgrading existing equipment, our technical specialists can provide detailed consultations to identify optimal automation strategies. Contact us at salescathy@sdhuashil.com to discuss your specific requirements and discover how HUASHIL automation technology can enhance your glass processing capabilities.
References
1. Johnson, Michael R. "Automation in Glass Processing: Technology Trends and Market Dynamics." Glass Manufacturing International, Vol. 45, No. 3, 2023, pp. 78-85.
2. Chen, Wei-Ming, and Sarah Thompson. "Precision Cutting Technologies for Architectural Glass Applications." Journal of Glass Science and Engineering, Vol. 28, No. 2, 2023, pp. 156-172.
3. Rodriguez, Carlos A. "Economic Analysis of Automated Glass Production Systems." Industrial Manufacturing Review, Vol. 67, No. 4, 2023, pp. 234-249.
4. Nakamura, Hiroshi, et al. "Quality Control in Automated Glass Fabrication Processes." Advanced Materials Processing, Vol. 41, No. 6, 2023, pp. 112-128.
5. Williams, Jennifer L. "Safety Considerations in Glass Processing Automation." Occupational Safety in Manufacturing, Vol. 33, No. 1, 2023, pp. 45-62.
6. Kumar, Rajesh, and Emma Fischer. "Integration Strategies for Glass Cutting Assembly Lines in Smart Factories." Automation Technology Today, Vol. 52, No. 8, 2023, pp. 189-205.